Elbow and Shoulder Specialist Zurich (Switzerland): Prof. Dr Karl Wieser
Treatment focus
- Reconstructions and joint-preserving replacement surgeries (tendon transfers) for rotator cuff tears
- Stabilization surgeries for shoulder joint instabilities
- Shoulder prosthesis in case of arthrosis or rheumatic diseases
- Bone fractures of the shoulder and elbow joint
- Elbow prosthesis (partial and total prosthesis)
- Complex elbow reconstruction
Contact
University Hospital Balgrist
Shoulder and Elbow Surgery
Forchstrasse 340, CH-8008 Zürich
P: +41 44 541 2726 F: +41 44 386 3009
Consultation Hours:
Monday – Friday
8.30 am – 12 Noon
1 pm – 5 pm

Medical Range
Range of Diagnostic Services
- Diagnostics of sports injuries
- Rheumatological diagnostics
- Orthopedic diagnostics
- Computer tomography
- MRI
- X-ray
- Ultrasound
- Electrophysiology
Range of Therapeutic Services
Elbow Surgery:
- Elbow arthroscopy
- Ligament reconstruction of the elbow joint
- Refixation of biceps tendon ruptures
- Treatment of elbow dislocation and fractures
- Treatment of tennis and golfer's elbow
- Elbow prosthesis
Shoulder Surgery:
- Shoulder arthroscopy
- Reconstruction of acute rotator cuff tears
- Joint preservation surgery for chronic rotator cuff tears (tendon transfers or replacement plastics)
- Treatment of fractures of the shoulder joint
- Treatment of acromioclavicular joint dislocation (AC joint dislocation)
- Treatment of degenerative shoulder diseases (e.g., shoulder arthrosis, calcified shoulder, frozen shoulder)
Endoprosthetics:
- Primary and revision prostheses of the elbow
- Primary and revision prostheses of the shoulder
More Information
Card
Prof. Dr Karl Wieser is an elbow and shoulder specialist and head of the shoulder and elbow surgery Section at University Hospital Balgrist.
Thanks to their own basic research and studies, the team led by Prof. Dr Karl Wieser offers highly specialized expertise in shoulder and elbow joint surgery for patients of all ages. The team of experts is frequently called upon in cases of acute complex joint damage caused by accidents or in the case of defective results of previous surgeries (revision operations). In particular, athletes in recreational and professional sports seek and find competent help from Prof. Dr Wieser and his team.
Shoulder Specialists for Arthroscopic or Open Surgery
The shoulder is a complex joint. Its control is comparatively vulnerable. The individual elements such as bones, muscles, tendons, cartilage, and ligaments are interconnected by complex joints, bursae, and sliding sheaths. Therefore, great accuracy and precise knowledge of the functional effects are required in treatment planning. Whenever possible, shoulder surgery is performed minimally invasive (arthroscopic) by Prof. Dr Wieser and his team. Endoscopic access to the shoulder joint reduces the risk of infection and speeds up the healing process.
Shoulder Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is performed to evaluate and operate on the shoulder joint and the space between the acromion and rotator cuff. To do this, a camera is inserted into the joint through a small incision in the skin. To make the structures more visible, the joint is filled with water. If necessary, working instruments are placed through further skin incisions. Meanwhile, highly complex procedures such as tendon replacement plastics or tendon transfers can be carried out using such an arthroscopic technique.
Arthroscopy of the shoulder is usually carried out under local anesthesia with the arm anesthetized. General anesthesia is usually not necessary, which supports early rehabilitation. The length of stay after the procedure is between one and three days. Significant improvement can be expected after six to twelve weeks.
Shoulder Dislocation
In a shoulder dislocation, the head of the humerus is dislocated from the socket. This can lead to a wide variety of consequential damage. First, there may be distension of the shoulder joint capsule and its ligaments, and detachment of the joint lip from the glenoid cavity. Furthermore, tears of the rotator cuff and nerve injury may occur.
After dislocation, the shoulder can often be stabilized with conservative therapies. However, in some cases, recurrent instability events occur, with the shoulder dislocating or not feeling stable with little outside input. This can be treated with either arthroscopic soft tissue surgery (Bankart surgery) or bone block stabilization (Latarjet), depending on the severity and functional demands. The team around Prof. Dr Wieser has a high level of expertise in this field due to scientific work and is considered an international reference center, especially in the complex cases that must be treated with bone block stabilization.
Rotator Cuff Rupture
The rotator cuff connects the shoulder blade with the upper arm and is responsible for abduction and rotation movements of the shoulder. In a rotator cuff rupture, one or more tendons that transmit muscle power from the shoulder blade to the humeral head rupture. Such a rupture often impairs the function of the shoulder and causes severe pain.
Such an injury does not necessarily require surgical treatment, but if the pain is experienced and function is impaired, there are several surgical treatment options in addition to conservative measures (e.g., physical therapy and infiltration therapies).
Most acute or subacute ruptures can be treated minimally invasively using shoulder arthroscopy. More complex or chronic ruptures often require more complex surgeries, such as tendon replacement plastics or tendon transfers. The latter was invented more than 25 years ago by the former head of University Hospital Balgrist and has undergone continuous technical modifications over the years and can now be performed arthroscopically to a large extent. This historical experience and the intensive basic scientific work have given University Hospital Balgrist an excellent international reputation and make Prof. Dr Wieser a sought-after speaker at national and international shoulder congresses.
Shoulder Prosthesis
A shoulder prosthesis is an artificial joint replacement that is inserted during orthopedic surgery. Among other things, such a prosthesis can be used to treat osteoarthritis, necrosis, tumors, complex bone fractures, and non-reconstructable rotator cuff ruptures. Depending on the damage to the shoulder joint, Prof. Dr Wieser and his team have various types of prostheses at their disposal.
In the case of osteoarthritis, an anatomical hemi- or total prosthesis is usually used. While in the case of complex bone fractures, the shoulder is replaced by a fracture prosthesis. The inverse total prosthesis is mainly used in patients with advanced osteoarthritis and simultaneous irreparable rotator cuff rupture. The University Hospital was one of the first hospitals in the world to use this type of prosthesis as a standard procedure; its patients have always been followed up at annual intervals for quality control purposes and the results have been published in international journals.
Experienced Elbow Specialist in Switzerland
The elbow joint is also vulnerable and exposed to high stress during sports and physical work. Dislocations and fractures are common. Fractures close to the joint that lead to dislocations must accordingly be surgically straightened and stabilized. Prof. Dr Wieser has great expertise in the field of elbow surgery.
Elbow Arthroscopy
Elbow arthroscopy is performed to assess and treat the interior of the joint including mucosal folds as well as cartilage condition and shape. To do this, a thin metal tube with a built-in lens system is inserted into the elbow joint through a small incision.
Arthroscopy of the elbow is mainly used to remove free joint bodies, thickened mucosal folds, and inflamed synovial membrane. Furthermore, arthroscopy is used to improve joint mobility and to operate on the tennis elbow.
The treatment usually takes place under partial anesthesia. Meanwhile, the blood supply of the arm is cut off, the joint is filled with fluid and the arthroscope is inserted. After only one to two days, the patient is allowed to leave the clinic.
Elbow Reconstruction
An elbow collateral ligament reconstruction is used to correct the instability of the elbow. Instabilities often occur after injuries to the collateral ligaments, such as those caused by elbow dislocations or heavy weight-bearing.
During the procedure, a freshly injured internal or external collateral ligament is sutured. In patients who have had instabilities for some time, the injured ligament is replaced with a tendon from the knee or forearm.
The elbow is immobilized for the initial seven to ten days after the procedure. Furthermore, it is recommended to wear a splint for six weeks. After that, physiotherapeutic measures can be started and after twelve weeks, strength building can begin.
Elbow Prosthesis
Severe wear and tear can occur over time in an elbow joint, as with any joint, causing movement restrictions and pain. An elbow prosthesis is used when damage to the joint cannot be reversed or surgically repaired.
The procedure is performed under either general or partial anesthesia. The affected arm is usually immobilized in a plaster splint for two days after the operation. After only six weeks, there is only minor discomfort, and the arm is functional again. In most cases, rehabilitation is complete after three months.
Please click here to visit the website of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery at University Hospital Balgrist.
Curriculum Vitae
| 2007 | Medical University of Graz |
| 2007–2008 | Assistant Physician for Surgery and Traumatology, Obwalden Cantonal Hospital |
| 2008–2009 | Assistant Physician for Surgery and Traumatology, Luzern Cantonal Hospital |
| 2010–2012 | Assistant Physician for Orthopedics, University Hospital Balgrist, Zurich |
| 2012 | Specialist Examination Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology of the Musculoskeletal System |
| 2013 | Senior Physician by Proxy for Orthopedics, University Hospital Balgrist, Zurich |
| 2013 | FMH for Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology of the Musculoskeletal System |
| 2014 | Further education title (FA) FMH Sports Medicine SGSM |
| 2015 | Venia Legendi University of Zurich |
| 2017 | Leading Physician Orthopaedics, University Hospital Balgrist, Zurich |
Click here for more information about Prof. Dr Wieser.
Team
- Prof. Dr Samy Bouaicha
Leading Physician Shoulder- and Elbow Surgery - Dr Jakob Ackermann
Senior Physician by Proxy Shoulder- and Elbow Surgery - Dr Bettina Hochreiter
Senior Physician Shoulder- and Elbow Surgery - Dr Philipp Kriechling
Senior Physician Shoulder- and Elbow Surgery
Extras
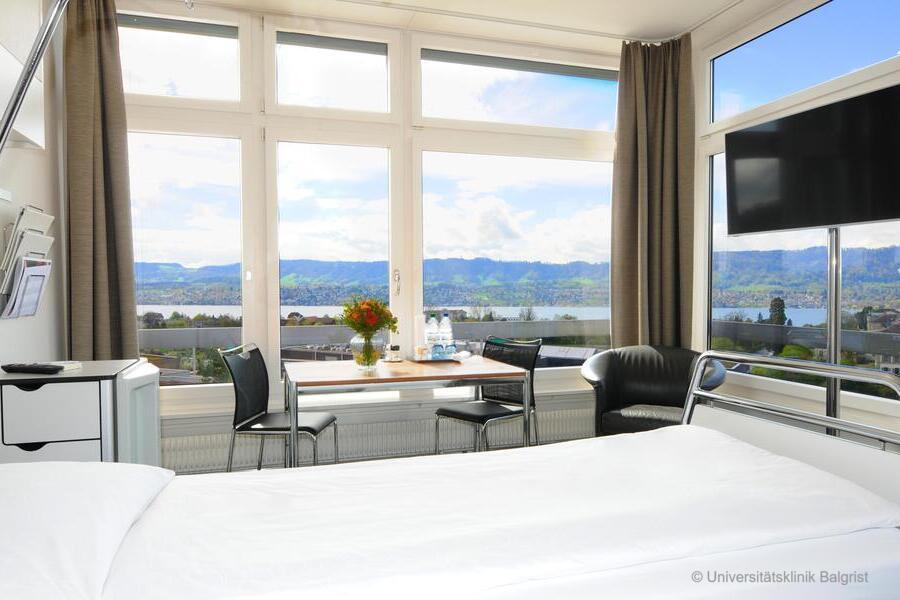
- Rooms with TV, telephone, WLAN, view of Lake Zurich
- Balgrist Café restaurant and cafeteria
- Comprehensive service for national and international guests
- Post office, kiosk
- Patient service (including tea and beverage service and organizing overnight stays for guests)
- Room service (for privately and semi-privately insured patients)
Transport Connections
| Zurich Main Station | 4,6 km |
| Zurich Airport | 14 km |
| Basel Airport | 105 km |
| Bern Belp Airport | 149 km |
| Geneva Airport | 288 km |
Information about Zurich
The capital of the canton of the same name is also the largest city in Switzerland. Geographically it is located north in eastern Switzerland. Zurich is situated on the Limmat River, directly at the outflow of Lake Zurich, and is thus also called the "Limmat City." Economically, socially and scientifically, Zurich is considered the center of Switzerland. Therefore, large banks, many media companies, and international companies are located there, and at the same time, the cultural offer is rich. The well-known Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich (ETHZ) gives Zurich an international name in educational institutions.