Rhythmology Leipzig (Saxony): PD Dr Kerstin Bode
Treatment focus
- Non-invasive diagnostics of cardiac arrhythmias, incl. cardiac MRI to clarify invasive diagnostics and therapy
- Electrophysiological examination
- Ablation (e.g., for atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, ectopic atrial tachycardia, AVNRT/AVRT/VT, extrasystoles)
- Implantation of event recorders, pacemakers, and defibrillators, along with conduction system pacing (CSP) and/or biventricular cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT)
- Revisions and extractions of event recorders, pacemakers, and defibrillators
- Treatment of pulmonary vein stenosis
Medical Range
Range of Diagnostic Services
- Long-term ECG
- Ergometry
- Tilt table
- Duplex
- TTE
- TEE
- Cardiac MRI
- EPS
Range of Therapeutic Services
- Ablation for atrial fibrillation
- Ablation for ventricular tachycardia (VT)
- Ablation for AV node reentry tachycardia
- Ablation for WPW syndrome
- Ablation for EAT - ectopic atrial tachycardia
- Ablation for ventricular extrasystoles (VES)
- Defibrillator insertion (transvenous, subcutaneous)
- Pacemaker insertion
- Extraction of pacemaker, ICD, and CRT systems
More Information
Card
PD med. Kerstin Bode is a specialist in cardiology and the head physician of the Department of Rhythmology at the Leipzig Heart Center.
Together with her experienced team, Dr Bode focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. The Rhythmology Department offers comprehensive diagnostic capabilities and employs the full range of modern treatment options for heart rhythm disorders. Patients benefit from the team's concentrated expertise and the advanced technology available at one of Europe's leading centers for rhythmology.
Detecting Heart Problems: Innovative Diagnostics without Intervention
PD Dr Kerstin Bode initially prefers non-invasive methods at the Leipzig Heart Center to accurately diagnose cardiac arrhythmias. Depending on the patient's symptoms and medical history, various examinations are carried out to create a precise picture of the heart's activity without the need for catheter-based intervention.
These diagnostic tools include, for example, a long-term ECG that records heart rhythms over 24 hours or longer and the Ajmaline test, which is used to detect certain congenital arrhythmias. A tilt table examination can help determine whether episodes of dizziness or fainting are related to circulatory dysregulation.
Physical exertion on a stationary bike, monitored via ECG, may be used to provoke rhythm disturbances or circulatory issues in the heart muscle. Additionally, cardiac ultrasound (echocardiography) is used to assess the heart's structure, wall motion, and valve function.
Based on the diagnostic findings, the medical team discusses the most suitable treatment options with the patient. These may range from lifestyle changes—such as healthier nutrition and increased physical activity—to rhythm-stabilizing medications or electrical cardioversion, a procedure that uses a controlled electric shock to restore normal heart rhythm.
Precisely Locating Cardiac Arrhythmias: Electrophysiology in Rhythmology Leipzig
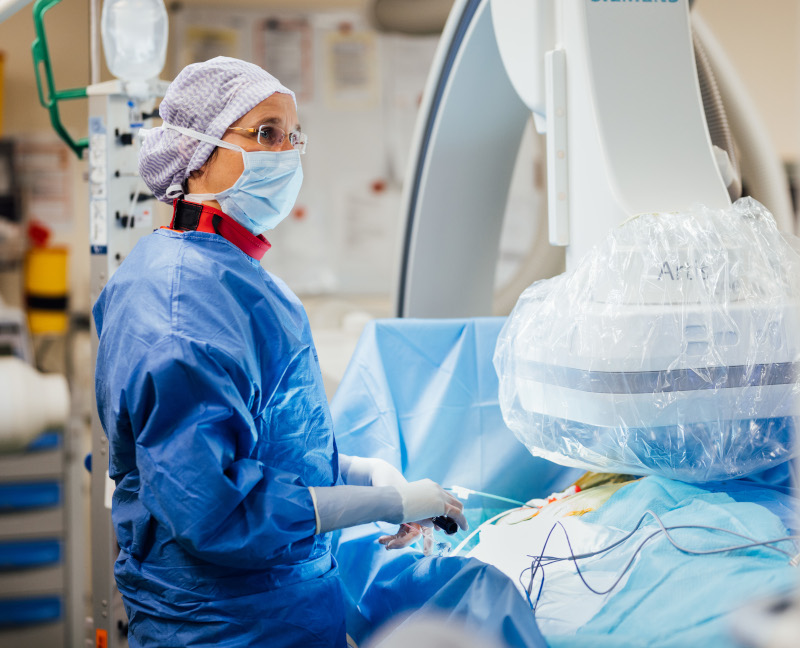
Electrophysiological examination (EPU) is a specialized cardiac catheterization procedure for the diagnosis and treatment of complex cardiac arrhythmias. It is carried out if an ECG cannot clarify the cause of the symptoms or as preparation for an ablation procedure, in which faulty tissue is selectively sclerosed.
Thin catheters are forwarded into the heart through the femoral vein in the groin area to record electrical signals directly from the heart muscle. If the disturbing arrhythmia does not occur during the examination, the doctor can trigger it with electrical impulses to determine the exact cause and localization. If the heartbeat is too fast, this can often be treated directly during the EPU.
The examination takes between 30 minutes and two hours. A pressure bandage is applied after the EPU to prevent bleeding. Complications such as minor bleeding or blood clots are rare. In most cases, triggered cardiac arrhythmias disappear on their own or can be treated directly.
Catheter Ablation in Leipzig – State-of-the-Art Therapy for Cardiac Arrhythmia
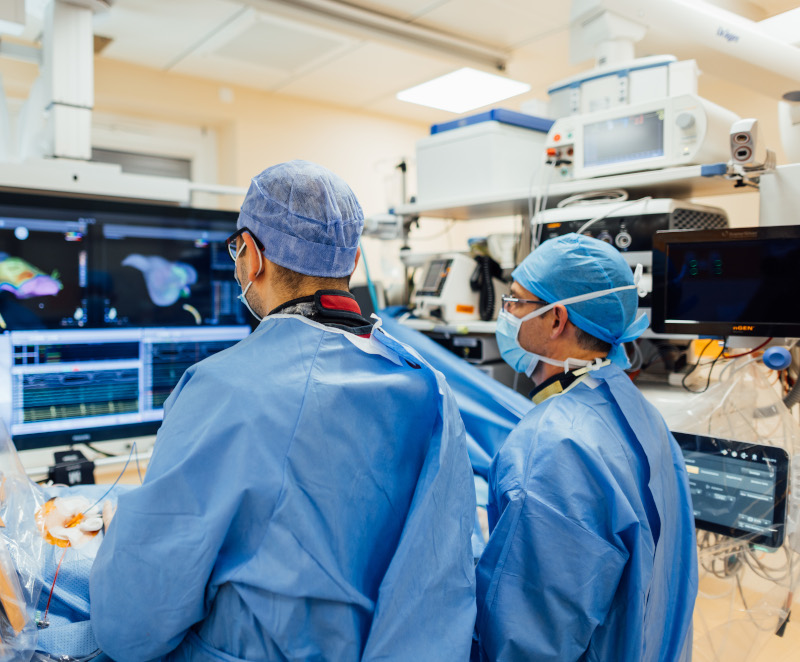
Catheter ablation is an innovative procedure for treating cardiac arrhythmias from the various heart chambers. Thin catheters are guided through the groin to the heart to selectively ablate the tissue that is causing the arrhythmia. This method is less stressful than open heart surgery.
During the procedure, patients are asleep, usually unaware of the procedure, and locally anesthetized at the access site in the groin. The affected areas of the heart are identified using high-precision 3D imaging. Various methods are used to remove the offending fibers specifically.
Radiofrequency ablation uses heat to ablate the tissue, while cryoablation uses extreme cold. A new method, pulsed-field ablation, uses electrical fields to treat only those heart muscle cells that are the cause of a conduction disorder. In this way, the surrounding heart muscle tissue can be spared as much as possible.
Ablation is highly effective and especially helpful for patients whose heart rhythm cannot be stabilized with medication alone. Risks are rare and include slight bleeding or, in very rare cases, injury to the esophagus or nerves. Thanks to the extensive experience of rhythmology specialist PD Dr Kerstin Bode and her team at Leipzig Heart Center, the treatment is particularly safe and effective.
Highest Level of Expertise in the Treatment of Pulmonary Vein Stenosis
Pulmonary vein stenosis is a rare complication following catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. This causes one or more pulmonary veins to narrow, which hinders the flow of blood from the lungs to the heart. This can lead to shortness of breath, coughing up blood, pneumonia, or fluid accumulation in the lungs.
To detect pulmonary vein stenosis at an early stage, the Leipzig Heart Center, a supra-regional specialist center, utilizes a unique cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging technique. This imaging precisely analyzes heart function, pulmonary vascular resistance, and blood flow to the lungs.
For this treatment, the constricted vein is dilated in the cardiac catheterization laboratory using a balloon catheter. This procedure is minimally invasive and is carried out via the inguinal vessels without the need for open surgery. In most cases, a stent is also implanted to keep the vessel open in the long term. Treatment success is reassessed the next day via radiological imaging, typically allowing for same-day discharge.
Specialist in Heart Implants – Event Recorders, Pacemakers & Defibrillators
PD Dr Kerstin Bode and her team have extensive experience in the implantation and use of event recorders, pacemakers, and defibrillators, including those with CRT and conduction system pacing capabilities. These devices are crucial for diagnosing and treating cardiac arrhythmias.
Pacemakers are used when the heart beats too slowly or when there are dangerous pauses in the heartbeat. The devices send electrical impulses to stabilize the heart rhythm and maintain a healthy pulse. The implantation is minimally invasive and can significantly improve the patient's quality of life.
Defibrillators (ICDs) are implanted to detect and automatically treat life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias. They can stop dangerous arrhythmias through targeted electric shocks and thus protect against sudden cardiac death.
Event recorders are small devices placed under the skin that continuously monitor the heart rhythm. They enable the long-term recording of irregularities that occur with sporadic symptoms, allowing for a precise diagnosis. This means that even sporadic arrhythmias can be detected and treated effectively. However, approval must be obtained from the health insurance company.
Dr. Bode's team, as a supra-regional center, has particular expertise in performing complex revision surgeries, including the extraction and explantation of pacemaker and defibrillator systems. This is necessary if electrodes are defective and need to be replaced or if the implanted system is infected and needs to be removed and then reinserted.
Curriculum Vitae
| December 2023 – present | Head Physician, Department of Rhythmology, Leipzig Heart Center |
| March 2023 – November 2023 | Acting Head Physician, Department of Rhythmology, Leipzig Heart Center |
| January 2023 – February 2023 | Senior Consultant, Department of Rhythmology, Leipzig Heart Center |
| 2021 - 2022 | Senior Consultant, Department of Cardiology, Rhythmology and Intensive Care Medicine, Asklepios Klinikum Weißenfels, Head of Focus Rhythmology |
| 2019 | Habilitation and Recognition as an Associate Professor |
| 2015 - 2020 | Senior Physician, Department of Rhythmology, Leipzig Heart Center, Head of the Department of, Among Others, Cardiac Electronic Implants, |
| 2015 - 2017 | University Studies of Health Economics, Outcomes Research and Management in Cardiovascular Science, London School of Economics, London, UK |
| 2015 | Specialist in Cardiology |
| 2011 | Specialist in Internal Medicine |
| 2005 - 2015 | Assistant/Specialist Physician in Internal Medicine/Cardiology, Leipzig Heart Center, Leipzig University, Helios Clinic Borna |
| 1995 - 2005 | Studies in Human Medicine, University of Leipzig |
Team
 PD Dr Sebastian Hilbert
PD Dr Sebastian Hilbert
Senior Consultant Department of Rhythmology
 PD Dr Sotirios Nedios
PD Dr Sotirios Nedios
Senior Consultant Department of Rhythmology
 Dr Michael Döring
Dr Michael Döring
Senior Physician Department of Rhythmology
 Prof. Dr Daniela Husser-Bollmann
Prof. Dr Daniela Husser-Bollmann
Senior Physician and Head of the Cardiocenter Rhythmology
 Prof. Dr Cosima Jahnke
Prof. Dr Cosima Jahnke
Senior Physician Department of Rhythmology
 Prof. Dr Ingo Paetsch
Prof. Dr Ingo Paetsch
Senior Physician Department of Rhythmology
 PD Dr Timm Seewöster
PD Dr Timm Seewöster
Senior Physician Department of Rhythmology
Extras
- Private and elective wards B3/B4 for private and elective patients as well as self-paying patients (outpatient and inpatient)
- Close, interdisciplinary cooperation with all departments of the Heart Center and Park Hospital to enable holistic diagnostics and treatment for patients
Transport Connections
| Leipzig Main Station | 8 km |
| Leipzig/Halle Airport | 30 km |
Medical Articles
This is the Rhythmology Department at the Heart Center Leipzig!
Head Physician Dr Kerstin Bode Presents the Department of Rhythmology.
Information about Leipzig
Leipzig is the largest city in Saxony and is located in the east of Germany. The historic city centre is particularly well preserved and some districts still date back to the Wilhelminian era. One of the largest alluvial forests in Central Europe runs through Leipzig - in the city, the area mainly extends along the Elster, Pleiße and Luppe rivers. Leipzig is world-famous as a trade fair centre, for example. The Leipzig exhibition centre is over 850 years old and is one of the oldest trade fair locations in the world.